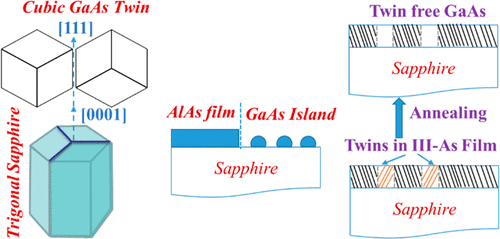
Crystalline Zinc Blende Gaas has been grown On trigonal c-plane sapphire substrate by molecular beam epitaxy. The Initial Stage of Gaas Thin Film Growth has been investigated extensively in this paper. When Grown on C-Plane Sapphire, It Takes (111) Crystal Orientation with Twinning as a major problem. Direct Growth of Gaas on Sapphire Results in Three-Dimensal Gaas Islands, Almost 50% Twin Volume, and a Weak in-Plane Correlation with the substrate. Introduction a Thin Alas Nucleation Layer Results in Complete Wetting of the Substrate, Better in-Plane Correlation with the substrate, and reduced Twinning to 16%. Further, we investigated the effect of growth temperature, pregrowth sapphire substrate surface, and in-situ annealing on the quality of the gaas epilayer. We have been able to reduce the twin volume below 2% and an x-ray Diffraction Rocking Curve Line Width to 223 Arcsec. A good quality gaas on sapphire can result in the implementation of microwave photonic functionality on photonic chip.
Discover