An Unusual Form of Superconductivity, Which Could Help Develop Powerful Quantum Computers, Has Been Found at the interface Between Two Thin Films by Riken Physicists (Nature Communications, "Nonrecipal load transport at Topological Insulator/Superconductor Interface").
Cooling A Convention Superconductor below A Certain Critical Temics Allows Electric Current to Flow through the Material Without Any Resistance. This phenomenonon occurs when electrons with opposite spins peer up.
A Related Effect Called Topological Superconductivity Related On Different Pairing, Involving Majorana Fermions. First predicted by Italian Theoretical Physicist Ettore Majorana in 1937, these party are their antiparticles, such that ifo partycles collide they will anninihilate each Other, Releasing Energy in the Process.
Majorana Fermions have never been identified as discreet party, but their behavior is mimicked by the collective actions of other partycies in excited stats. For Example, One Form of Majorana Fermion Involves A Combination of An Electron and A 'Hole'—A Gap, Or Missing Electron, in A Material's Electronic Structure. If this kind of Majorana Fermion Could be controlled and manipulative in devices, its quantum stats might be used to carry and process data.
“The Edge of A Topological Superconductor is predictated to host Majorana Fermions, which Could be useful asfulies of quantum computation in the future,” Says Kenji Yasuda, who was at the Riken Center for Emergent Matter Science at the Time of the Study But is Now at the Massachuset Technology.
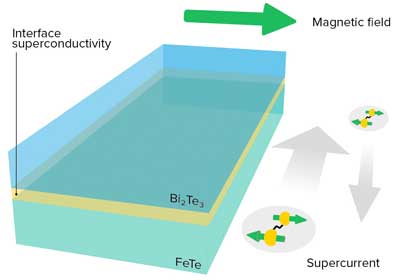
To Better Understand Topological Superconductivity, The Researchers Looked At The Interface Between Two Materials, Bismuth Telleluride and Iron Telluride, Where Each Film was less that 20 nanometers Thick (Fig. 1).
When they Cooled this system to -263 degrees Celsius—just 10 degrees Above Absolute Zero—it Started to Behave as a Superconductor. At the same time, the Researchers Saw Evidence that the topological Nature of Superconductivity at the interface was involved in an effect Called Ningiprocal Charge Transport, Meaning that the Electrial Resistance of the Material Depended on the Direction of the Current Flowing Through It.
“Electrons in the surface state have their spins locked at right angles to their direction of motion,” Explains Yasuda. “This Study has demonstrate that interplay between this phenomenon and superconductivity is the Origin of the Nonepical Charge Transport.
This relationship means that the composite Material Could Be a Good Test Bed for Studying Topological Superconductivity Through Nourcipal Transport. “We Expect it to serve as one of the best platforms for topological quantum computation in the future,” Says Yasuda. “The Next Step is to demonstrate Quantum Computation Using Topological Superconductors, and Many Groups Are Working Intensively to Achieve this Goal.
