Computers process information based on arrays of so-called bits. Each bit can take the values of one or zero. This is typically realized with integrated electronic circuits permanently written onto a semiconductor chip.
Researchers from Paderborn University and Technical University Dortmund have now realized an all-optical bit that is temporarily written into a planar semiconductor nanostructure only using light and that can also be reconfigured only using optical techniques.
Besides the fundamental interest, this new approach carries promise for future optoelectronic application schemes.
The results are now published in the scientific journal Nature Communications (« Realization of all-optical vortex switching in exciton-polariton condensates »).
Rotation direction of the vortex carries the binary information
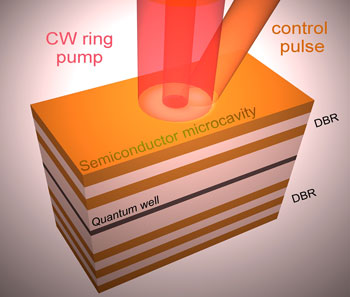
In the present study the research teams of Prof. Stefan Schumacher (Paderborn University) and Prof. Marc Aßmann (Technical University Dortmund) investigate a particular type of vortex state forming inside a quantum fluid excited in a planar semiconductor nanostructure.
“The vortices that form can rotate in two different directions. These two directions are then associated with the two values of a bit, zero or one, respectively,” explains the PI Prof. Schumacher.
The structure is optically excitated with a ring-shaped laser profile, the vortex forming resides in the center of the ring. An additional short laser pulse is then applied to invert the rotation direction of the vortex. This way the optical bit can be reconfigured or switched from zero to one and vice versa.
Switching takes the billionth part of a second
With their promise for information storage or processing, similar vortex states are currently also being studied in a number of other systems.
“Quite often, however, only the existence or creation of the vortex states is investigated. Here, we also demonstrate the efficient control with ultrashort laser pulses. We can actually switch the rotation direction of the vortex and the information stored within the billionth part of a second,” elaborates the first author, Dr. Ma.
“A particular achievement of the present study is the practical and robust implementation of the scheme in the lab. The rotation direction of the vortex is directly measured through the orbital angular momentum of the light emitted,” notes Bernd Berger, who has developed the optical setup as part of his PhD studies at the TU Dortmund.
The general concept only requires off-resonant and therefore incoherent optical excitation, which also makes it compatible with electrical approaches.
The theoretical idea was developed by the first author, Dr. Xuekai Ma. In close collaboration with the group of Prof. Aßmann in Dortmund, the scheme was then successfully realized in the lab.
“I am delighted that Dr. Ma was again successful in bringing one of his ideas to fruition and in publishing it in such a highly regarded scientific journal,” states his advisor Prof. Schumacher.
Previously Dr. Ma received the „Chinese government award for outstanding PhD students“ for his PhD studies that he completed at Paderborn University in 2017. In the past, his work was also published in the Physical Review Letters on multiple occasions.
Dr. Ma carries out his numerically demanding computations on the super computers of the Paderborn Center for Parallel Computing, PC2. The semiconductor nanostructure used in the experiments was grown at the University of Würzburg; the theory work was performed in collaboration with the group of Prof. T. Meier at Paderborn University.
The present work is part of the joint project “Nonlinear Cavity Polariton Physics for Functional Photonic Elements” of the groups of Prof. Schumacher (Paderborn University) and Prof. Aßmann (TU Dortmund) and is funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) within the Collaborative Research Center TRR142 “Tailored Nonlinear Photonics”.
Source: Universität Paderborn
